Mankind Stepping into Future
The 20th and 21st centuries have been defined by humanity's relentless pursuit of technological advancement, often driven by competition and conflict. Like Faust's deal with Mephistopheles, our greatest innovations have come at a price: progress purchased through peril. Behind every moon landing, nuclear reactor, and neural network lies a story of geopolitical rivalry, ideological clashes, and desperate gambles for supremacy. These were not mere engineering feats - they were existential chess matches where the stakes ranged from global dominance to species survival.
The Space Race: When Humanity United in Looking Up (1950s-1970s)
In the shadow of post-war tensions, humanity found an unexpected path to progress through rivalry. The Space Race, seemingly a contest between the United States and Soviet Union, became something far more profound: humanity's first coordinated step into the cosmos. While rooted in Cold War competition, it sparked a revolution in human achievement that transcended political boundaries.
A Tale of Two Powers
The story begins with a simple beep - the sound of Sputnik 1 broadcasting from orbit in 1957. This modest sphere, no larger than a beach ball, represented the Soviet Union's opening move in what would become the greatest technological competition in history. The message was clear: the final frontier was now open for exploration.
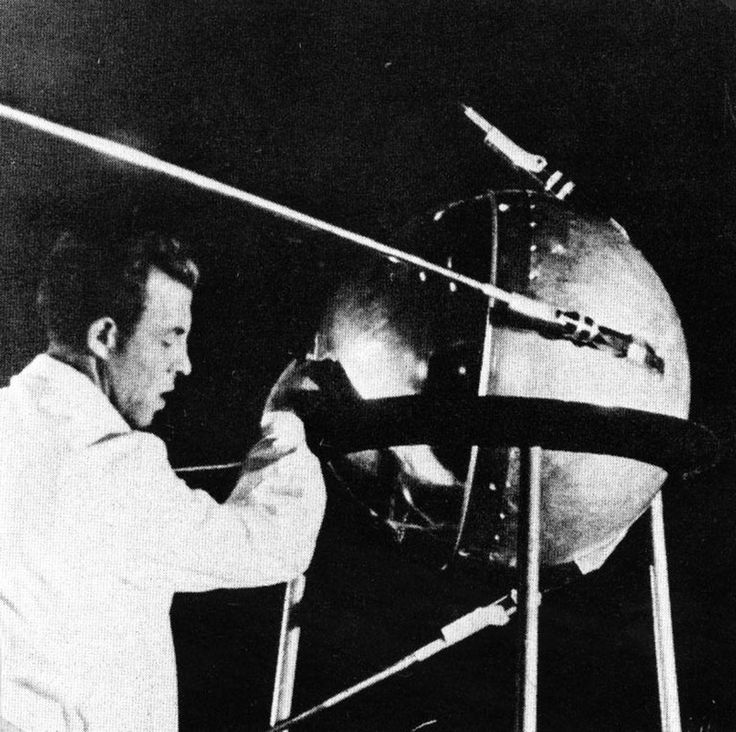

Key Milestones


The pace of innovation was breathtaking:
- 1957: Sputnik 1's metallic heartbeat echoes across the globe, marking humanity's first venture beyond the atmosphere
- 1961: Yuri Gagarin's historic flight proves that humans can survive in space, opening the door to countless possibilities
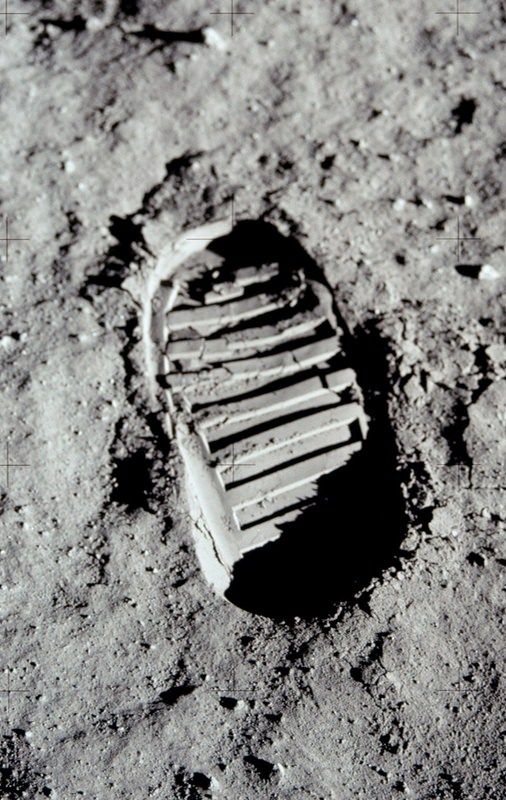
- 1969: The Apollo 11 mission achieves what was once thought impossible - human boots on lunar soil, with Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin taking those historic steps
The Nuclear Arms Race: Power of the Atom (1940s-1990s)
In the aftermath of World War II, two superpowers embarked on a dangerous dance with the atom. The Nuclear Age emerged from the ashes of Hiroshima and Nagasaki - not as a story of scientific triumph, but as a stark reminder of humanity's capacity for both creation and destruction.
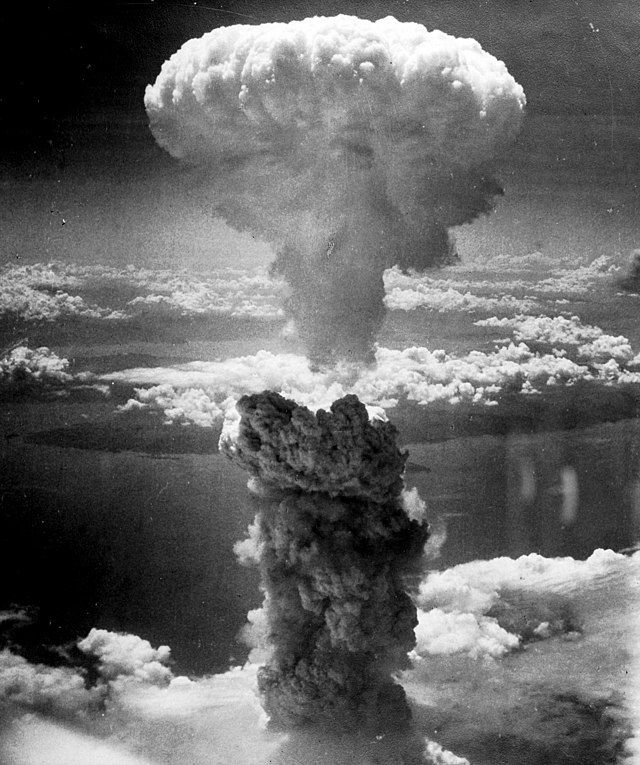


The Path of the Atom
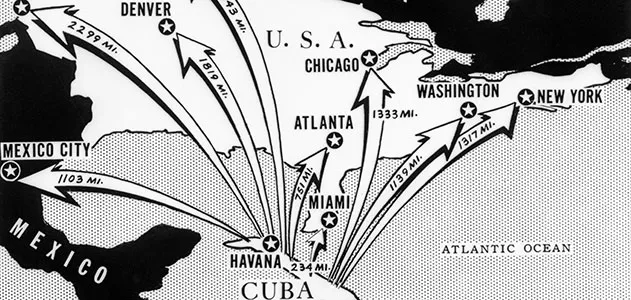
The nuclear story unfolded across decades, with each development carrying profound implications for humanity:
- 1945: The atomic age dawns with Hiroshima and Nagasaki - a moment that forever changed warfare
- 1949: Soviet atomic success ends U.S. monopoly, beginning an era of nuclear parity
- 1952-53: Hydrogen bomb tests by both superpowers raise stakes exponentially
- 1962: Cuban Missile Crisis brings humanity to the brink, teaching unforgettable lessons about nuclear risks
The Computer and Internet Revolution: Birth of a Digital Planet (1970s-2000s)
The Digital Revolution marked humanity's third great leap forward. After nuclear physics and space exploration, computing emerged to reshape human consciousness itself. From California garages came the power to extend human thought through silicon and code. What began as a counterculture movement spawned tech giants like Google and Facebook, who became the new architects of human experience. The computer evolved from tool to a force that would fundamentally transform civilization.
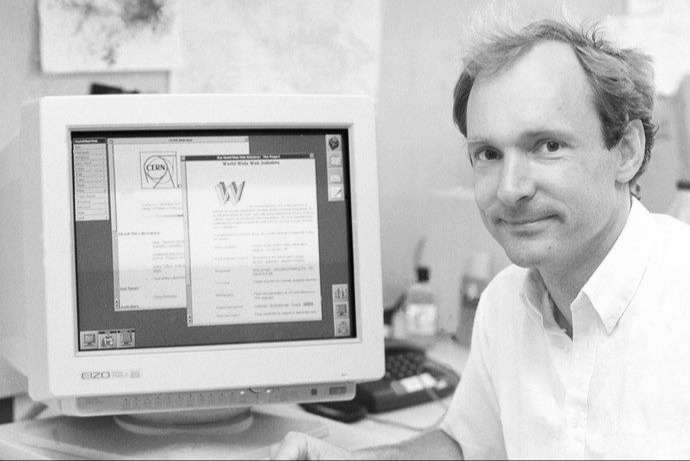
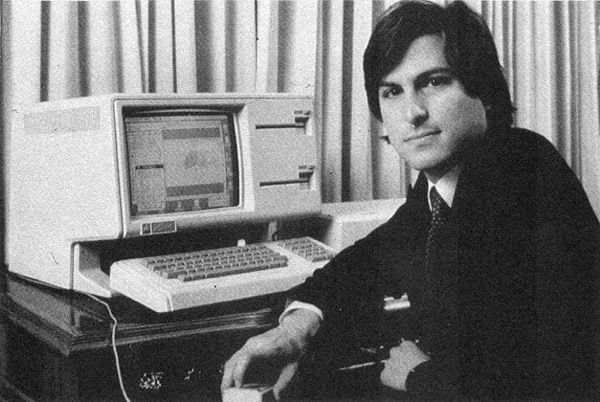


The Digital Dawn
The computer revolution unfolded in waves, each reshaping humanity's relationship with technology:
- 1970s: Personal computing emerges from Silicon Valley garages - Apple and IBM make computers personal
- 1980s: Japan dominates semiconductors, controlling 50% of global chip production
- 1991: Tim Berners-Lee's World Wide Web connects humanity through the internet
- 2000s: China rises as a tech powerhouse, dominating electronics manufacturing
The AI Race: Dawn of Machine Intelligence (2010s-Present)
In the quiet laboratories of the early 2010s, a profound transformation began to take shape. Neural networks, once confined to academic research papers, suddenly demonstrated capabilities that bordered on the miraculous. This wasn't merely another technological advancement - we were creating new forms of intelligence that could think, reason, and create in ways we had never imagined possible.
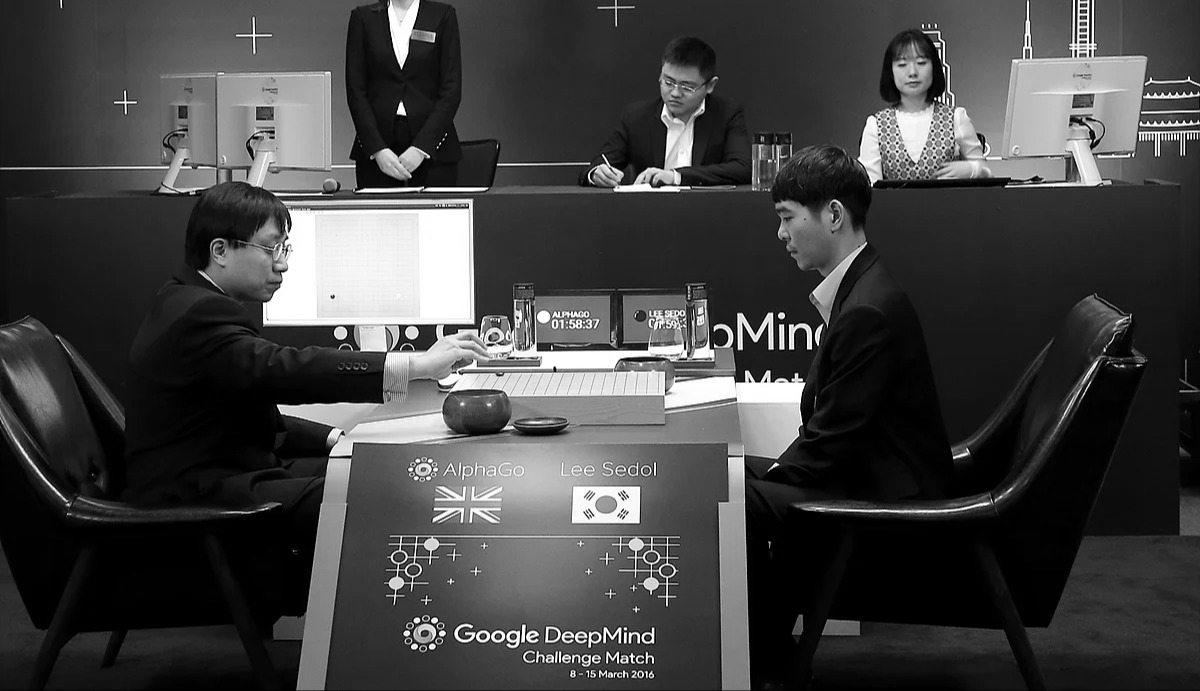


The Intelligence Revolution
The AI revolution unfolded with unprecedented speed, marking perhaps the most profound shift in human capability since the invention of writing:
- 2012: Deep learning breakthrough as AlexNet masters image recognition, launching the modern AI era
- 2016: AlphaGo defeats world champion Lee Sedol, demonstrating AI's mastery of complex strategy
- 2022: ChatGPT reaches 100 million users in two months, bringing AI into everyday life
- 2025: China's Deepseek R1 model challenges Western AI dominance, marking a new phase in global AI competition
Like the nuclear revolution before it, AI development raises profound questions about humanity's future. But unlike previous technological leaps that extended our physical reach, AI amplifies our very capacity to think and create - marking the dawn of a new chapter in human evolution.
The Next Chapter: A New World Order (2025-)
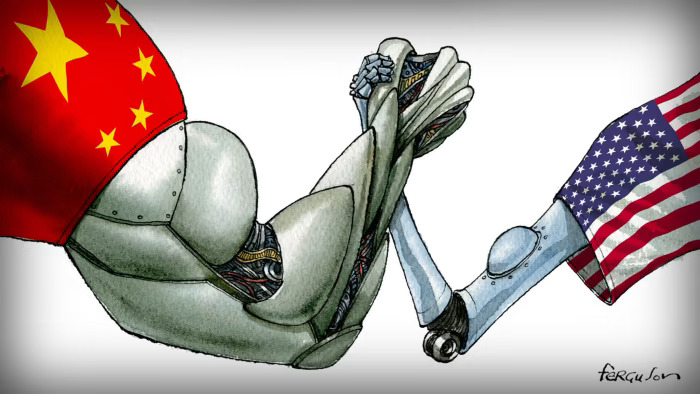
As the decade unfolds, a new bipolar world emerges - not defined by nuclear arsenals, but by AI capabilities. The United States and China stand as the dominant forces, each pursuing different visions of AI's future. Silicon Valley champions commercial innovation, while China's state-directed but open approach emphasizes national strategic advantages. The stakes of this technological cold war extend beyond economic supremacy to fundamental questions about the very nature of human society.
Epilogue: The Convergence of Revolutions

The Legacy of Innovation
The Space Age (1950s-1970s)
- Satellite networks enabling global communications
- Space-based Earth observation and climate monitoring
The Nuclear Era (1940s-1990s)
- Clean energy powering modern civilization
- Medical breakthroughs saving countless lives
The Digital Revolution (1970s-2000s)
- Global internet connectivity
- Mobile computing transformation